How Allergies and Skin Conditions Lead to Ear Lumps
- Leadraft SEO
- Oct 14, 2025
- 6 min read
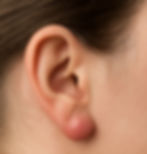
Finding a lump near or on your ear can be unsettling. While many lumps are harmless and temporary, others may be a sign of an underlying issue that needs attention. Among the most common causes are allergies and skin conditions. Both can lead to inflammation, infection, or cyst formation that presents as a lump on or around the ear.
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore how allergies and skin conditions contribute to ear lumps, the different types, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures to help keep your ears healthy.
Understanding Ear Lumps
An ear lump is a localized swelling or raised bump that appears on the ear’s surface, behind the ear, or even inside the ear canal. The lump can be hard or soft, painful or painless, small or large — depending on the cause.
While most ear lumps are benign, they shouldn’t be ignored. They can be caused by:
Allergic reactions
Skin infections
Cysts or benign growths
Acne or blocked pores
Inflammation from trauma or irritation
Allergies and chronic skin conditions can create an environment where swelling,
cysts, or bumps easily form, particularly in the delicate skin around the ears.
The Link Between Allergies and Ear Lumps
1. What Happens During an Allergic Reaction
An allergic reaction occurs when the immune system identifies a normally harmless substance — such as pollen, dust, metal, or certain foods — as a threat. The body releases histamines, leading to inflammation, itching, and swelling.
When the skin around the ear or inside the ear canal reacts to allergens, this inflammatory response can cause lumps or bumps to form. These may appear red, itchy, or painful, and sometimes filled with fluid or pus if infection develops.
2. Contact Dermatitis from Jewelry or Products
One of the most common allergic causes of ear lumps is contact dermatitis — a skin reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an allergen or irritant.
Metal Allergies: Earrings made of nickel or non-hypoallergenic metals are a leading trigger. The earlobe may swell, itch, and develop a small lump or cyst-like bump.
Hair and Skincare Products: Shampoos, hair sprays, gels, or perfumes that contain alcohol or artificial fragrances can irritate the skin behind the ears, leading to redness, rashes, and bumps.
Hearing Aids or Earphones: Some materials in ear molds or earphones can cause irritation inside the ear canal.
3. Food and Environmental Allergies
Food allergies or seasonal allergies can indirectly lead to ear lumps by triggering lymph node swelling around the ear and neck. When the immune system reacts to allergens, lymph nodes near the ear may enlarge, forming tender lumps that can
persist for several days.
4. Allergic Otitis Externa
In some cases, allergies lead to otitis externa, or inflammation of the outer ear canal. Allergic otitis externa can result from exposure to allergens in water, ear drops, or hearing devices. Symptoms include:
Itching or burning inside the ear
Fluid discharge
Redness and swelling
A lump or swelling near the ear opening
Left untreated, allergic otitis externa can become infected, worsening discomfort and swelling.
Common Skin Conditions That Cause Ear Lumps
Beyond allergies, several skin conditions can lead to ear lumps. These disorders may affect the skin surface, hair follicles, or oil glands around the ear, leading to swelling, nodules, or cyst formation.
1. Sebaceous Cysts
A sebaceous cyst is one of the most common causes of ear lumps. It occurs when sebaceous glands that produce oil (sebum) become blocked. The trapped sebum forms a small, round lump under the skin, usually painless unless infected.
These cysts often appear on the earlobe or behind the ear and may grow slowly over time. In some cases, they can become red, tender, and filled with pus if bacteria enter the cyst.
2. Acne and Folliculitis
Acne doesn’t just affect the face; it can also appear around the ears. When hair follicles become clogged with oil, dirt, or dead skin cells, small pimples or lumps form.
Folliculitis, a related condition, occurs when hair follicles become inflamed due to bacterial or fungal infection. This results in red, itchy, and sometimes painful bumps that can resemble ear lumps.
3. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. When eczema affects the ears, it can lead to:
Crusty or scaly patches on or behind the ear
Small bumps that ooze fluid
Thickened skin from repeated scratching
Persistent inflammation from eczema can cause swelling that feels like a lump, especially behind the ear.
4. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is another chronic condition that causes overproduction of skin cells, resulting in thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. Psoriasis behind or around the ears can cause raised lesions that feel like lumps.
In severe cases, psoriasis may extend into the ear canal, causing discomfort and temporary hearing issues.
5. Keloids and Scar Tissue
After ear piercings or injuries, some individuals develop keloids — thick, raised areas of scar tissue that grow beyond the original wound site. These firm, shiny lumps can appear on the earlobe or behind the ear and are often itchy or tender.
Symptoms That May Accompany Ear Lumps
Depending on the cause, ear lumps may be accompanied by several symptoms:
Itching or redness
Pain or tenderness
Fluid discharge or crusting
Warmth or swelling
Scaling or flaking skin
Fever (in case of infection)
Hearing changes if the lump is inside the canal
Persistent or painful lumps, especially those that grow over time or are accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever, require medical attention.
Diagnosing Ear Lumps
A correct diagnosis is key to proper treatment. Doctors typically follow a step-by-step process to identify the cause of an ear lump:
Physical Examination: The doctor inspects the lump’s size, color, texture, and location.
Medical History: They review any recent infections, allergies, or skin issues.
Allergy Testing: For recurrent allergic ear lumps, patch or prick tests may identify triggers.
Skin Biopsy: In chronic or unusual cases, a small skin sample is analyzed under a microscope.
Imaging Tests: If a deep infection or cyst is suspected, ultrasound or MRI may be used.
Accurate diagnosis helps differentiate allergic reactions from bacterial or fungal infections and determines the appropriate treatment approach.
Treatment Options for Ear Lumps
Treatment depends on the underlying cause — whether allergy-related or a skin condition.
1. Managing Allergic Reactions
Antihistamines: Help reduce swelling and itching caused by allergic reactions.
Topical Corticosteroids: Creams or ointments relieve inflammation from contact dermatitis or eczema.
Avoiding Allergens: Switching to hypoallergenic jewelry, fragrance-free shampoos, or gentle cleansers can prevent recurrence.
Cold Compress: Applying a cool compress helps soothe itching and swelling.
2. Treating Skin Conditions
Topical Antibiotics: Used for infected cysts, acne, or folliculitis.
Moisturizers: Hydrating creams help control eczema and dryness.
Medicated Shampoos: Coal tar or salicylic acid shampoos help manage psoriasis around the ears.
Minor Surgery: Sebaceous cysts or keloids may require surgical removal if large or persistent.
3. Addressing Infections
If the lump is infected:
Oral antibiotics may be prescribed.
Warm compresses can help drain pus.
Proper hygiene and avoiding picking or squeezing the lump prevent worsening.
4. Medical Treatments at Hospitals
For severe or chronic cases, specialized care from dermatologists or ENT specialists is essential. Facilities like Vamshodaya Hospitals offer advanced diagnostic tools, allergy testing, and minimally invasive treatments to safely manage ear lumps caused by allergic or skin conditions.
Preventing Ear Lumps from Allergies and Skin Conditions
Use Hypoallergenic Products: Choose earrings and skincare products labeled as nickel-free or hypoallergenic.
Maintain Ear Hygiene: Clean your ears and earrings regularly but avoid over-cleaning, which can irritate the skin.
Moisturize Regularly: Prevent dryness that can lead to eczema or cracking.
Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Stay away from hair dyes, sprays, and products with alcohol or artificial fragrance.
Manage Allergies: Take preventive medications during allergy seasons and avoid known triggers.
Treat Skin Conditions Promptly: Managing eczema or psoriasis early prevents secondary infections and lump formation.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if you notice:
Rapidly growing or painful lumps
Lumps that persist beyond two weeks
Discharge, bleeding, or crust formation
Fever or swelling around the neck
Hearing difficulties or ear canal blockage
Early diagnosis prevents complications and ensures the best possible outcome.
Ear lumps can arise from a variety of causes, but allergies and skin conditions are among the most common culprits. Whether it’s contact dermatitis from earrings, eczema flare-ups, or sebaceous cysts due to blocked oil glands, understanding the cause helps determine effective treatment.
Proper ear hygiene, awareness of triggers, and timely medical attention are vital to preventing and managing ear lumps. If you’re dealing with persistent or painful lumps, consult a qualified dermatologist or ENT specialist for diagnosis and care.
By addressing both allergies and underlying skin issues, you can maintain healthy, irritation-free ears and prevent future occurrences.





.png)